Tracing Guide
The ability to trace your code is essential for debugging. Given some arbitrary Python code, you should always be able to answer the questions:
- What line gets executed next?
- What is the current state of memory? In other words, which values are currently assigned to which variables?
Instructions
Trace the execution of a program by filling in a tracing table.
- In Step, number the step of execution.
- In Memory State, show the values of all variables currently in memory after the line has executed, e.g.,
x: 5 - In Next Line, write down the next line of code that will execute, e.g., 2.
- In Output, write down any text if any, that will be printed.
Tracing table:
| Step | Memory State | Next Line | Output |
Example 1
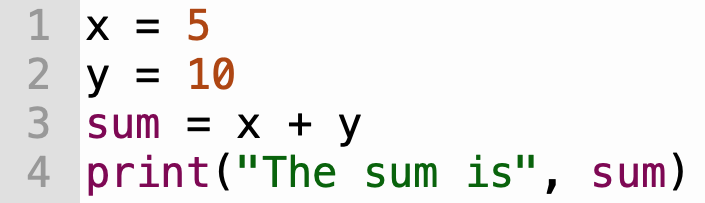
| Step | Memory State | Next Line | Output |
| 1 | x: 5 | 2 | |
| 2 | x: 5, y: 10 | 3 | |
| 3 | x: 5, y: 10, sum: 15 | 4 | |
| 4 | x: 5, y: 10, sum: 15 | Done | The sum is 15 |
Example 2

| Step | Memory State | Next Line | Output |
| 1 | x: 5 | 2 | |
| 2 | x: 5 | 4 | |
| 3 | x: 5 | 5 | |
| 4 | x: 5, result = "Odd" | 6 | |
| 5 | x: 5, result = "Odd" | Done | Odd |